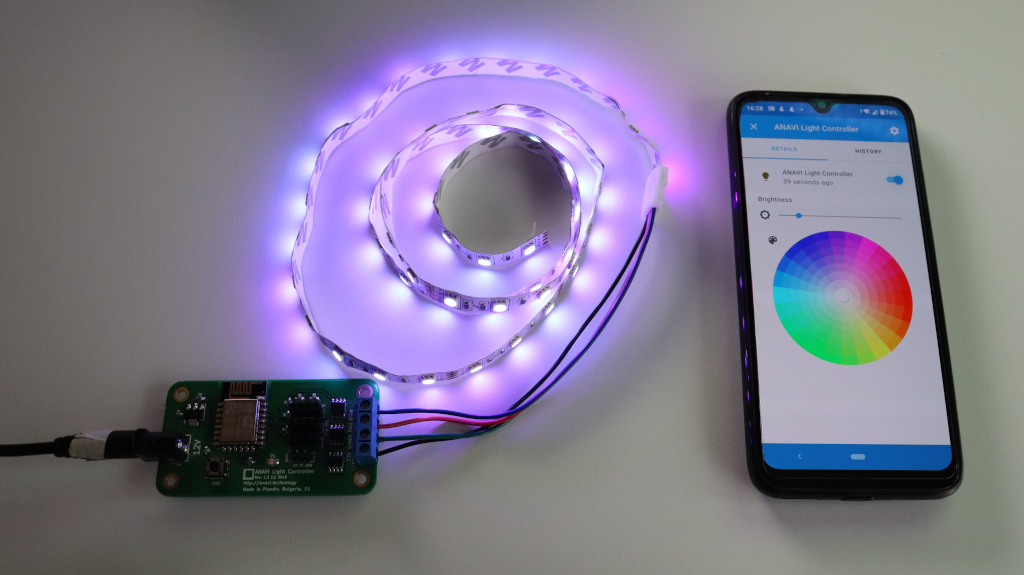
ESPHome is an open-source firmware ecosystem that lets you easily control microcontrollers through simple YAML configurations. It is best known for its excellent support for the ESP8266 and ESP32 families, powering countless DIY and smart-home projects. However, ESPHome has also been ported to additional hardware platforms. Exploring one of these alternatives was the motivation behind this small project.
One such alternative is the WB3S, a Tuya Wi-Fi module built around the Beken BK7231T microcontroller. It offers 15 GPIOs (including 6 PWM, 2 UART, and an ADC) and conveniently shares the same footprint as the popular ESP-12 modules based on ESP8266 which you know from ANAVI Thermometer, ANAVI Light Controller and several other of our boards. Thanks to the open-source LibreTiny PlatformIO environment, ESPHome can be built and flashed for WB3S and other Beken-based modules.
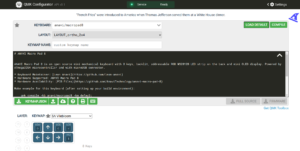
As part of this exploration, I designed an open source WB3S breakout board, fully compatible with breadboard prototyping and created in KiCad. In the accompanying demo video and example configuration, I walk through the entire workflow: designing the board, setting up the software environment, compiling the firmware with ESPHome, and flashing it to the module using ltchiptool.
The example ESPHome configuration used in the video is available here. Replace SSID and PASSWORD with your Wi-Fi credentials.
Conclusion
Our new WB3S breakout board is available in GitHub as open hardware for anyone interested in experimenting with the BK7231T and ESPHome. However, while functional, ESPHome support for Beken-based devices still lags far behind the mature and reliable ESP32 ecosystem. For production projects or anything requiring stability, it is highly recommended sticking with ESP32 for now.