WLED is a powerful open-source firmware that makes managing NeoPixel WS2812B LED panels simple and efficient. Designed for ESP32 and ESP8266, it provides an intuitive interface for seamless LED control. Whether you’re a DIY enthusiast or a professional, WLED offers a highly customizable lighting experience.
Why Choose WLED for NeoPixel LED Panels?
Our previous blog post shared the exact steps how to install WLED directly from a web browser. This firmware includes a built-in local HTTP server, allowing LED control from any device on the same network. It also integrates smoothly with Home Assistant, enabling smart home automation, voice control, and advanced lighting effects. WLED supports both LED strips and 2D LED matrices, making it a versatile choice for various lighting projects.
Demo: ANAVI Miracle Emitter + XIAO ESP32C3
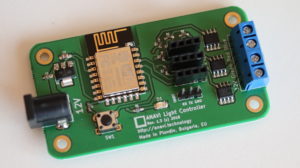
In this tutorial, we will walk through the setup and configuration of NeoPixel WS2812B LED panels using WLED firmware. The demonstration features the open source hardware ANAVI Miracle Emitter, an open-source IoT board designed specifically for controlling NeoPixel LEDs.
Hardware & Accessories Used:
- ANAVI Miracle Emitter – A small ESP32C3-based board, ideal for WLED applications.
- NeoPixel WS2812B LED Panels – High-quality, customizable LED panels.
- Wago Splicing Connectors – Secure and easy wiring connections.
- DC Barrel Jack to Terminal Block Adapter – Simplifies power connections. For example AP364 or from Pololu.
- External 5V Power Supply – Powers both the LED panels and the development board.
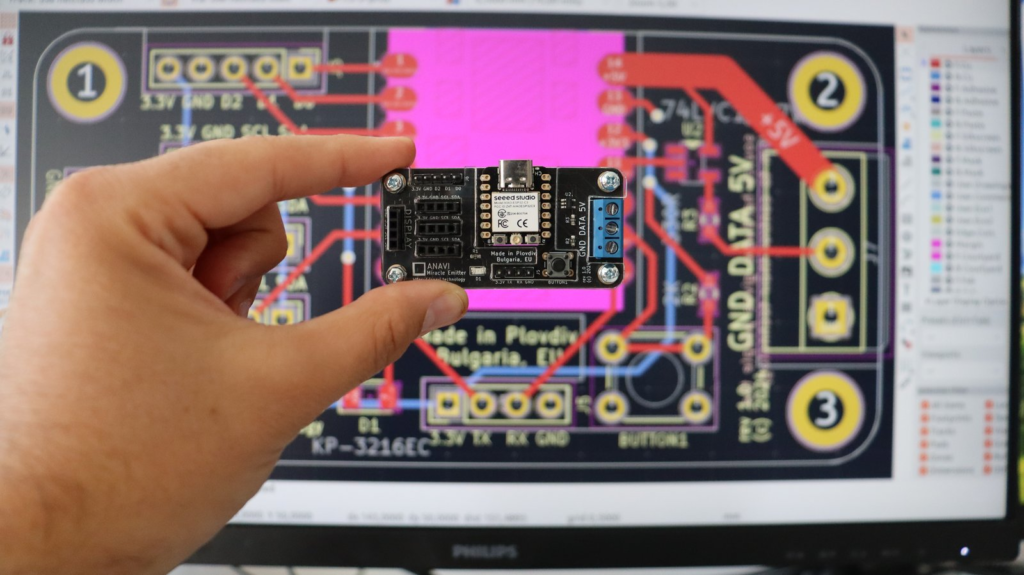
ANAVI Miracle Emitter: Open-Source LED Controller
ANAVI Miracle Emitter is a compact open-source IoT board built for NeoPixel LED control. It also supports I2C sensors and a mini OLED display, making it a great choice for interactive projects. Designed using KiCad, this board will soon be available through a Crowd Supply crowdfunding campaign. If you’re looking for a powerful and compact way to control NeoPixel WS2812B LED panels, the ANAVI Miracle Emitter with WLED is an excellent solution. The XIAO ESP32C3, with its 32-bit RISC-V core, delivers strong performance in a small package, making it ideal for compact LED projects. Stay tuned for more tutorials on maximizing WLED and the ANAVI Miracle Emitter for your next LED lighting setup.