ANAVI Gas Detector is an ESP8266-powered, open source, Wi-Fi development board for monitoring air quality and detecting dangerous gases. After a very successful crowdfunding campaign at Crowd Supply we are manufacturing a batch of units in Plovdiv, Bulgaria. All kits of ANAVI Gas Detector also include MQ-135 sensor module, USB to UART debug cable, an acrylic stand and a mini OLED I2C display. In this article you will learn how to get started and assemble all parts in about 10 minutes.
The printed circuit board of ANAVI Gas Detector has the same dimensions as the one for my other open source product ANAVI Thermometer so actually both use the same laser cut acrylic stand. Both ANAVI Gas Detector and ANAVI Thermometer have been designed using the open source software KiCAD. The open source software OpenSCAD was used to design the case.
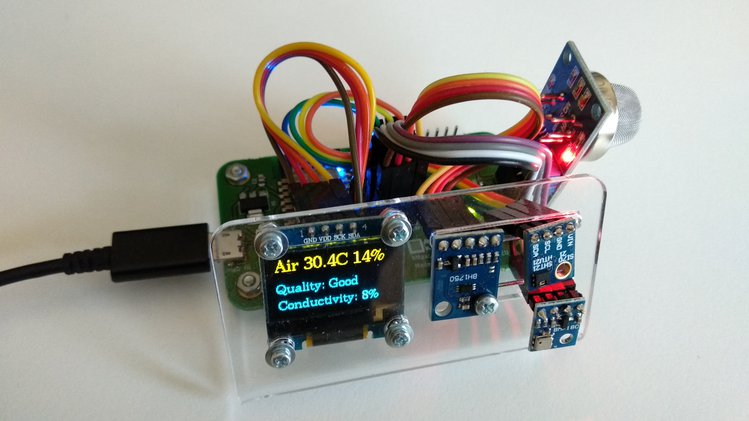
In this article you will learn the exact steps how to assembly ANAVI Gas Detector Starter Kit. The procedure is the pretty much the same for Advanced and Developer kits, however they including additional I2C sensor modules. Appropriate nuts, screws and washers are included in all kits.
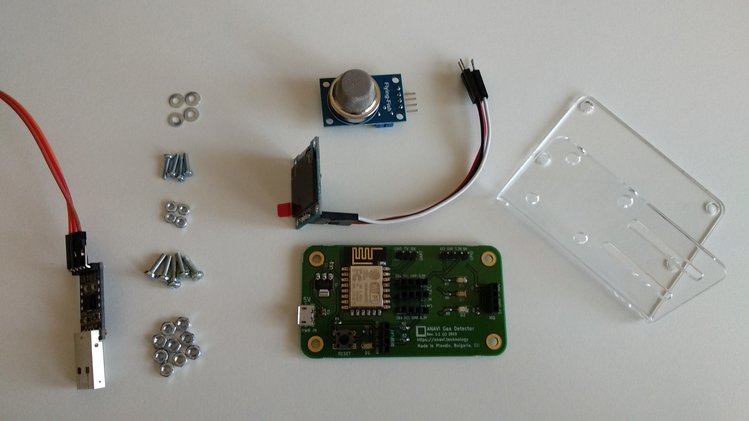

Step 1
Peel off the protective film from the acrylic stand. Also remove the protective film from the display.
Step 2
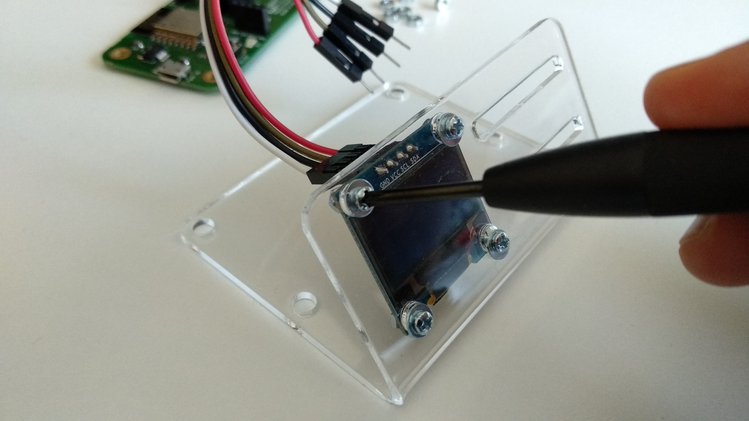
Using a screwdriver, gently attach the mini OLED display to the acrylic stand with the M2 screws and nuts as shown on the photo. The mini OLED display is fragile so please be very careful. Do NOT fasten it too tight because the torque may break it.
Step 3
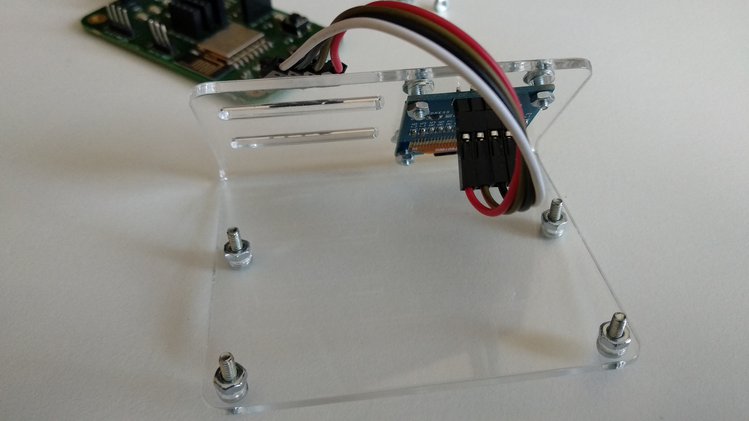

Add four M2.5 screws and nuts to the case of the acrylic stand. In the next step we will put ANAVI Gas Detector on top of the nuts.
Step 4
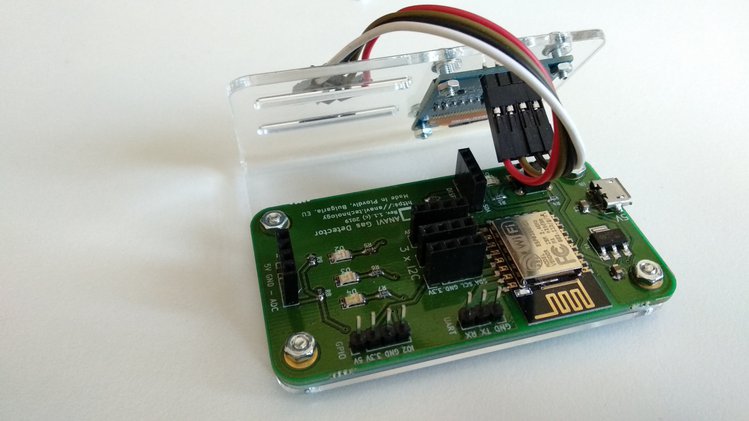

Add ANAVI Gas Detector on top of the nuts and fasten it with the additional M2.5 nuts. At the end you will have a spare M2.5 screw and nut to optionally attach an additional sensor to the acrylic enclosure.
Step 5
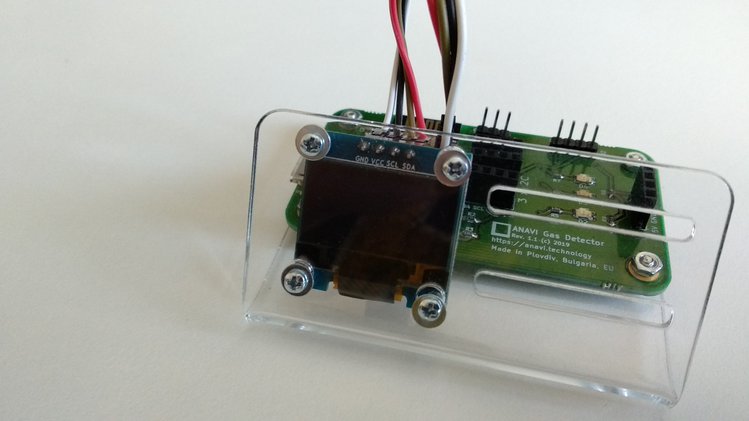
Gently connect the mini OLED display to the dedicated slot using the male to female jumper wires. The colors of the wires do not matter. Just have a look at the labels on the top of the OLED display and connect each of the four pins to a pin with the same label on the dedicated slot for the display on ANAVI Gas Detector.
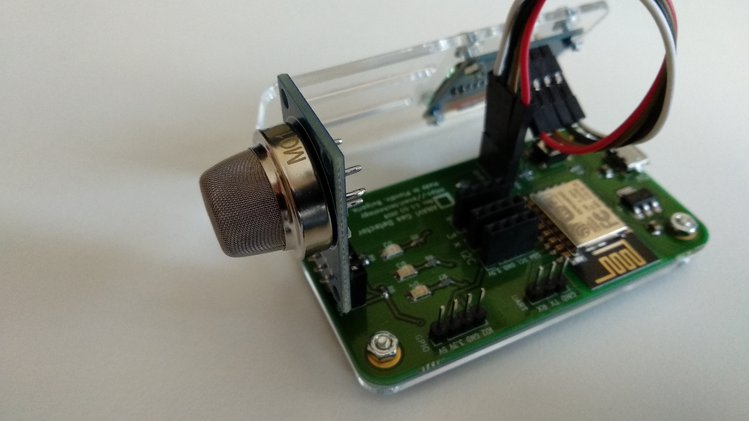

Plug the MQ-135 sensor module in slot labeled as MQ. Owners of Advanced or Developer kit should also plug the additional I2C sensor modules.
Finally, you are ready to turn on and enjoy ANAVI Gas Detector!
On first boot you need to calibrate MQ-135 and configure and connect ANAVI Gas Detector to your WiFi network.
The so called “burn-in” procedure for initial calibration of MQ-135 is important to be done on first boot. Despite its fancy name it is actually quite easy. Just place ANAVI Gas Detector with MQ-135 sensor module in a room with clean air and leave it running for at least 24 hours. This has to be done only once when MQ-135 sensor module is used for the first time. After doing this procedure, on every next boot ANAVI Gas Detector and MQ-135 will do a quick calibration in couple of minutes and start working properly.
We have also published this tutorial as an update at Crowd Supply to notify all backers of ANAVI Gas Detector. The whole user’s manual for ANAVI Gas Detector is available at GitHub. This is an entirely open source project so as usual ideas for improvements and bug fixes are always welcome!





2 thoughts on “ANAVI Gas Detector Assembly Guide”
Comments are closed.